In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) stands as a critical line of defence against a myriad of cyber threats. However, a pressing concern emerges: what happens when the defender itself becomes the target? This question is at the heart of a groundbreaking study by researchers Khushnaseeb Roshan, Aasim Zafar, and Sheikh Burhan Ul Haque, who delve into the vulnerabilities of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models within NIDS frameworks.
Adversarial Machine Learning (AML) represents a burgeoning field where malicious actors craft adversarial examples to deceive ML and DL models, leading to incorrect predictions. These adversarial perturbations pose significant challenges to the robustness and reliability of NIDS, particularly in real-time and mission-critical applications. The researchers’ work aims to shed light on the intricacies of adversarial attacks and the defence strategies necessary to fortify NIDS against such threats.
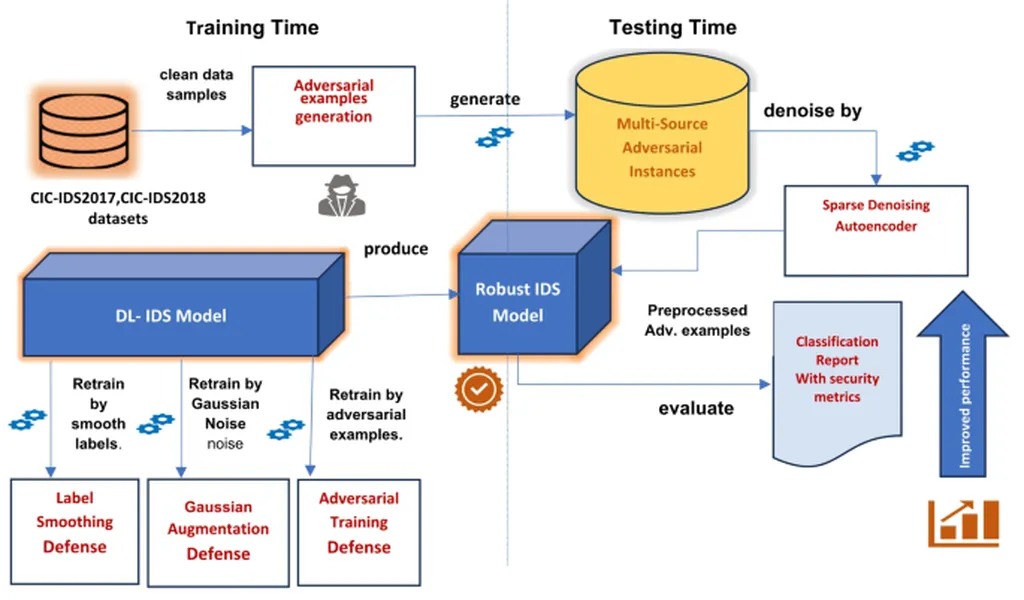
The study implements four powerful adversarial attack techniques: Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM), Jacobian Saliency Map Attack (JSMA), Projected Gradient Descent (PGD), and Carlini & Wagner (C&W). Each method was rigorously analysed to assess its impact on NIDS performance using various metrics. The findings reveal the potential vulnerabilities of current NIDS models when subjected to these sophisticated attacks.
To counter these threats, the researchers explored three heuristic defence strategies: Adversarial Training (AT), Gaussian Data Augmentation (GDA), and High Confidence (HC). These methods were implemented to enhance the robustness of NIDS in adversarial scenarios. By integrating these defence mechanisms, the study provides a comprehensive framework for improving the resilience of ML and DL-based NIDS against adversarial attacks.
The research underscores the importance of understanding and mitigating adversarial threats in real-time network environments. The complete workflow, including data packet flow, was demonstrated to highlight the practical applications and effectiveness of the proposed defence strategies. This work not only advances the field of AML but also offers valuable insights for researchers and practitioners focused on computer network security.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for robust and adaptive defence mechanisms becomes increasingly critical. This study serves as a vital contribution to the ongoing efforts to safeguard computer networks from the ever-growing array of cybersecurity threats, ensuring that our digital infrastructures remain secure in an increasingly interconnected world. Read the original research paper here.